About Gum Ghatti
We want to share our enthusiasm for our flagship product, gum ghatti, with you. No natural or chemically synthesized product can offer this natural gum's unique properties and multi-faceted functionality. Our team aims to provide our customers with the highest-quality material while ensuring sustainable and ethical sourcing and delivering tailored customer service.
What is Gum Ghatti?
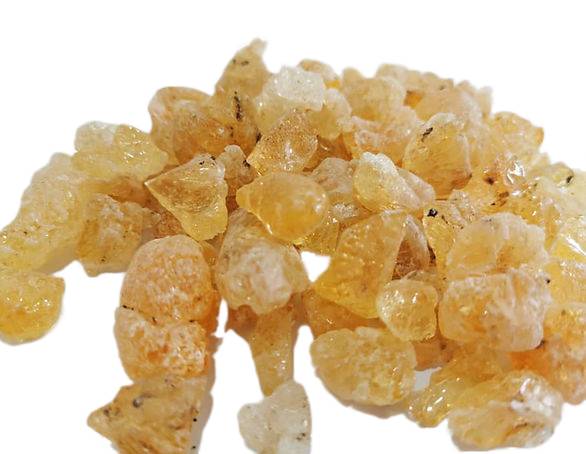
Gum Ghatti is a complex polysaccharide famous for its unique properties and the applications of gum ghatti are extended to various industries because of its versatility. Gum Ghatti has several other names in various languages and regions. Gum ghatti is known as "Dhawda" in India because Anogeissus latifolia (the tree from which gum ghatti is obtained) is locally called as "Dhawda" in Indian local languages. In the French language, Gum Ghatti is known as "gomme ghatti". As such it is also known as “Goma Ghatti” in Spanish. It is an organic gum that acts as a natural stabilizer, natural emulsifier and natural thickener making it a versatile agent that can be applied in different industries from the food industries to the pharmaceutical sector, where it is employed as a binder or a film-forming agent.
Gum Ghatti is an Excellent Substitute of Gum Arabic / Gum Acacia
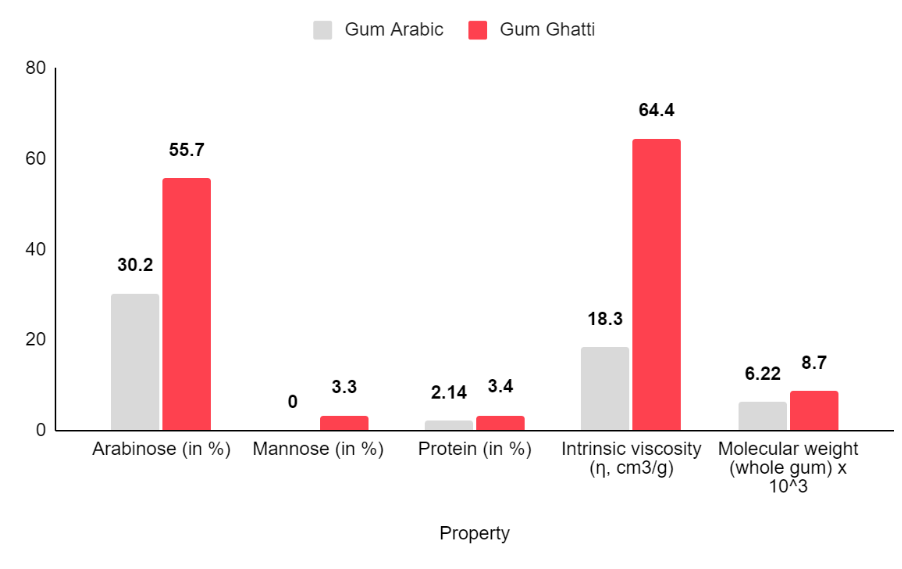
Gum ghatti is a superior alternative to Gum Arabic which is also known as Gum Acacia. As a superior substitute of Gum Arabic, Gum Ghatti provides 4x better emulsification and stabilization capacity. Another reason why it is the best alternative to Gum Acacia is because the price of Gum Ghatti is comparatively less than Gum Arabic. One of the advantages of gum ghatti it is highly soluble in water compared to Gum Arabic which allows it to dissolve both in hot and cold water making it an absolute substitute of Gum Acacia.
Origins and Harvesting
Gum Ghatti is the amorphous translucent exudate of the Anogeissus Latifolia tree, a member of the Combretaceae family. The tree occurs throughout much of India, more commonly in dry deciduous forests.
Gum extracted from Anogeissus Latifolia tree is locally called “Dhawda” in India. The color varies from whitish-yellow to amber depending on factors like the proximity of the tear to the bark, the length of time it has remained on the tree before being picked, and the age of the product in storage.
The exudates are hand-picked by the locals and laid to dry in the sun for several days before being delivered directly or via authorized forest contractors to our processing plants.

Chemical Properties and Solubility
Gum Ghatti is a complex polysaccharide of high molecular weight. It occurs naturally as a mix of calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium salt. Complete hydrolysis has shown that it is composed of L-arabinose, D-galactose, D-mannose, D-xylose, and D-glucoronic acid in a molar ratio of 10:6:2:1:2 plus traces less than 1% of 6-deoxyhexose.
Gum Ghatti is a water-soluble gum that can be dispersed in hot or cold water to form a colloidal solution. It dissolves in water by 80 to 90%. Small amounts of acid or alkali do not affect ghatti dispersions, as the gum acts as a buffer and reverts to its normal pH of about 4.8. Additionally, Ghatti shows good emulsifying properties.
Gum Ghatti 4X BETTER PERFORMANCE COMPARED TO GUM ARABIC
Gum Ghatti is often considered and used as a superior alternative to Gum Arabic/Acacia due to its 4X better emulsification and stabilization capacity. Moreover, these gums are also used synergistically together to reduce costs while maintaining the same viscosity.